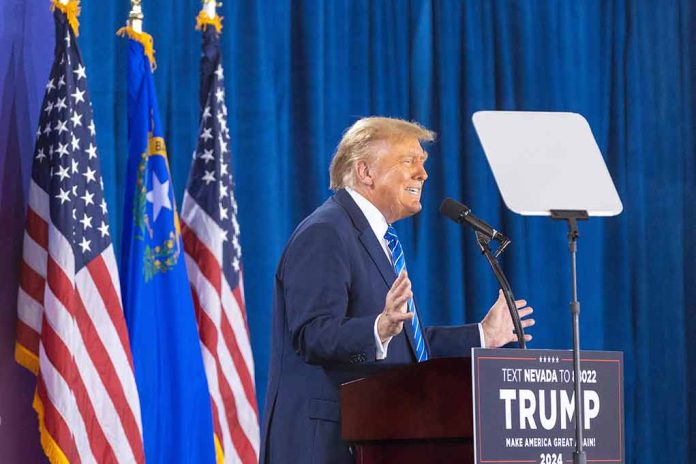
President Trump delivers on his promise to reduce federal control of education with a bold $12 billion cut to the Department of Education’s 2026 budget, setting the stage for eventual departmental dissolution despite judicial resistance.
Key Takeaways
- The Trump administration’s 2026 budget proposal slashes Department of Education funding by 15.3%, reducing it to $66.7 billion as part of the “skinny budget” initiative
- The proposal consolidates 18 smaller K-12 programs into one grant, cutting their combined funding from $6.5 billion to $2 billion
- Maximum Federal Pell Grants would decrease from $7,400 to $5,700, and the Federal Work-Study program faces an 80% funding cut
- Title I funding for high-poverty districts remains unchanged at $18 billion, while IDEA funding appears increased but effectively remains flat
- The budget reflects President Trump’s commitment to returning education authority to individual states
Federal Education Control Being Dismantled
The U.S. Department of Education released its comprehensive fiscal year 2026 budget proposal on May 30, expanding on the administration’s earlier “skinny budget” framework. The proposal requests $66.7 billion, representing a substantial $12 billion reduction from 2025 funding levels. This 15.3% decrease aligns perfectly with President Trump’s campaign promises to reduce federal overreach in education and return control to state and local authorities where it constitutionally belongs. The proposal represents the most significant step toward dismantling federal education bureaucracy in decades.
“We’re going to be returning education very simply back to the states where it belongs,” Said President Trump.
This budget blueprint comes despite a federal judge temporarily blocking the president’s executive order to close the Department of Education, demonstrating the administration’s unwavering commitment to fulfilling campaign promises through multiple avenues. The proposal strategically maintains certain funding priorities while dramatically reducing or eliminating programs considered beyond the proper scope of federal involvement, sending a clear message about the administration’s constitutional approach to governance.
Strategic Funding Priorities
The budget proposal strategically maintains Title I funding at over $18 billion, ensuring continued support for school districts serving high-poverty areas. This decision reflects the administration’s commitment to addressing genuine educational disparities while eliminating wasteful programs that have failed to deliver results. Simultaneously, the proposal smartly consolidates 18 smaller K-12 programs into a single block grant, reducing their combined funding from $6.5 billion to $2 billion while giving states greater flexibility in how these resources are allocated.
Funding for the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) appears to increase to $14.9 billion, but this figure includes several previously separate programs being folded in, resulting in effectively flat funding for special education services. This restructuring represents a more streamlined approach to special education funding while maintaining essential services. The proposal reflects careful consideration of which programs deliver genuine value to students versus those that primarily sustain the educational bureaucracy.
Higher Education Reform
The higher education landscape faces significant changes under the proposed budget, with reforms targeting bloated financial aid programs that have contributed to skyrocketing college costs. The maximum Federal Pell Grant would be reduced from $7,400 to $5,700, an adjustment that recognizes how federal aid has enabled universities to continuously raise tuition rates. The Federal Work-Study program would see an 80% reduction in funding, with colleges expected to cover most of students’ wages—a change that shifts responsibility back to the institutions benefiting from student enrollment.
“reverses decades of commitment to the promise of the Higher Education Act and would result in considerable harm for students pursuing postsecondary education,” Said Melanie Storey, a critic of the budget cuts.
Critics of the reductions predictably claim these cuts will harm students, but they conveniently ignore how decades of increasing federal subsidies have enabled the higher education industry to dramatically inflate tuition costs. By reducing federal involvement, the administration aims to force colleges and universities to compete on cost and quality, ultimately making higher education more affordable and valuable. This market-based approach represents a fundamental shift from the failed policies that have created today’s student debt crisis.
Returning Authority to the States
The budget proposal’s most significant impact may be its philosophical alignment with constitutional principles. By dramatically reducing federal education staffing and responsibilities, the Trump administration is reversing decades of unconstitutional federal overreach into what should be state and local decisions. The Constitution does not enumerate education as a federal power, making the Department of Education’s extensive regulatory apparatus constitutionally questionable. This budget represents a return to proper constitutional order and recognizes that education decisions are best made closest to the students they affect.
State education departments will gain increased authority and flexibility under this proposal, allowing educational approaches tailored to regional needs rather than one-size-fits-all federal mandates. This shift acknowledges the tremendous diversity across America’s educational landscape and empowers communities to develop solutions appropriate to their unique circumstances. As the proposal moves through the budget process, it signals the beginning of a fundamental transformation in how education governance functions in America—one that respects both constitutional boundaries and the principle of local control.